Chapter 1 – Computer Systems and Information Technology
In today’s tech-driven world, foundational knowledge of computer systems, computer networking, and information technology (IT) helps educators be more effective, resilient, and proactive in supporting their students and themselves. It is increasingly essential for educators because it empowers them to enhance teaching, improve classroom management, and prepare students for the digital world. Familiarity with standard operating systems is a foundation for teaching and learning. Applications, or software, allow users to complete tasks via a graphical, user-friendly environment. Some applications come pre-installed on computers, but the user must install additional software. Various types of software allow users to complete different tasks, from office productivity software like Microsoft Word and Excel to multimedia editing software like Adobe Photoshop and Premiere Pro, to virus protection software like Norton and McAfee. There is likely a software application for almost any task imaginable on a computer.
Computer Networks
Computer networking refers to multiple devices (e.g., desktop computers, mobile devices, routers, or applications) connected to transmit and exchange resources and information. Networked devices can share information over physical or wireless connections. Basic types of networks include a local area network (LAN), a wide area network (WAN), and a wireless network (Wi-Fi).
Before current network practices, computer engineers would have to move computers to share data between devices physically. This was a challenging task at the time because computers were large and cumbersome. The United States Government needed to find a way to simplify the process. The Department of Defense funded a project, hiring the best communication researchers and engineers to create the first operational computer network, named the ARPANET, in the late 1960s (Ibm, 2025). Advancements in networking practices and computer systems have evolved tremendously. The computer networks of today’s world are large-scale and have inter-device communication to meet every need. Many technologies, such as the Internet, searching online, email, shopping online, live-streaming capability, and social media, all exist because of advancements in computer networking.
Types of networks:
- LAN (Local Area Network): A network within a small geographic area like a school or classroom.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): A more extensive network spanning regions, like the Internet. Cloud networks are another example of a WAN.
- Wi-Fi (Wireless Network): A wireless technology enabling devices to connect to the Internet or a network without cables.
Other key concepts in computer networking include:
- Router: Directs traffic between devices on the Internet
- Switch: Connects multiple devices in a LAN
- Firewall: Safeguards networks by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic from the network
Operating Systems
An operating system is the most critical software that runs on a computer. It manages the computer’s memory and processes, as well as all of its hardware and software. A computer’s operating system allows the user to communicate with the device. Without an operating system, a computer is useless.
Watch this video to learn more about a computer’s operating system:
When a computer is purchased, an operating system is usually pre-loaded. Think Microsoft Windows on a PC. Most people use the operating system on their computer; however, the user can upgrade or change operating systems.
The three most common operating systems for personal computers are:
-
- Microsoft Windows
- MacOS
- Linux
Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface or GUI (pronounced gooey). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus. Everything is displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text. The following briefly overviews the three most common operating systems for desktop or laptop computers.
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft created the Windows operating system in the mid-1980s. There have been many versions over the years, the most recent being Windows 10, released in 2015. Microsoft Windows typically comes pre-loaded on most new PCs, making it the most popular operating system in the world.
macOS
The macOS is a series of operating systems created by Apple. This operating system comes pre-loaded on all Macintosh or Mac computers. The most recent versions of the macOS were released in 2016, 2017, and 2018. Sequoia (2025) is the newest macOS available. Most people like the look and feel of the macOS over the Windows operating system; however, Mac users account for a much smaller percentage than Windows users. Mac computers are higher priced, which may account for a smaller percentage.
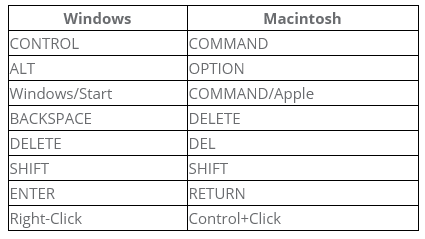
Operating systems are continually updated, and the features and design are intended to be enhanced with each update. However, the basics of working with computing devices have remained the same over the past decade. The Windows and Mac OS operating systems are relatively similar at the user interface level. Below is a table showing how the shortcut keys align between the two:
Linux
Linux (pronounced LINN-ux) is a family of open-source operating systems. This means they can be modified and distributed to anyone worldwide. Linux is different from proprietary operating systems like Windows, which can only be modified by the company that owns it.
Operating Systems for Mobile Devices
Mobile devices, such as iPads, tablets, and smartphones, run on operating systems designed specifically for mobile devices. Examples of mobile operating systems include Apple iOS and Google Android.
Apps, as commonly used for mobile device applications, are purchased from the Apple App Store or Google Play (for Android). Apps can be installed for free or paid.
Files
A computer file is a self-contained information available to the operating system and any number of programs. Knowing the file type you work with on a computer is always essential.
Like within Microsoft Office applications, media-generating applications typically have proprietary file types (the files only work on their software) but can also export to various other generic formats. For example, Adobe Photoshop, the leading photo editing application in the industry today, has a proprietary tile of .psd. However, many other photo editing programs will not open a .psd file. There are certain advantages to saving a file in its proprietary format. Still, if another application needs to open the file, it should be saved to one of the more universal image file types.
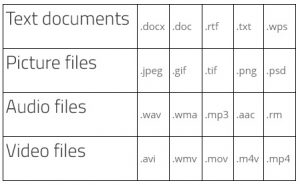
Today, there are many categories of files and specific types within each category. The following table is an example of some of the different categories and the more commonly known types:
Read this article from Khan Academy to learn about computer files, file types, and file sizes.
Portable Document Format (PDF)
The PDF file format is used when you save files that cannot be modified but still need to be easily shared and printed. PDF is a file format that operates independently of software, hardware, and the operating system. The PDF will present and exchange documents reliably, regardless of the software, hardware, or operating system. For example, if I create a flyer using the fonts and design elements available on my computer but then send it to another computer, there is a good chance it will not look the same on the other computer because of various hardware/software differences. If I save the flyer as a PDF and open it on another computer, it will look the same. This is why PDFs are so commonly used on the Internet. Now you know why teachers use PDF documents often! Adobe Acrobat Reader is the default program for reading PDF documents and is available on almost all computers.
The PDF format was created by Adobe, along with the software to view PDF files, Adobe Acrobat. There are various levels of Adobe Acrobat, starting from Reader, which is free and allows you to open PDF documents. The Acrobat reader is typically pre-installed on most computer devices, and it only allows you to view PDF files. Then, there are additional versions of Adobe Acrobat that can be purchased, which allow a user to create PDF files, including fillable PDF forms. For more information on the Acrobat family, refer to http://www.adobe.com/products/acrobat. Though the Reader may have come pre-installed on your computer, it must be updated occasionally. Adobe Reader can be downloaded or updated from the following website: https://get.adobe.com/reader/ .
More current applications now include creating PDF files directly from the application itself. For example, starting in 2007, Microsoft Office programs like Word, PowerPoint, and Excel included the option to choose a PDF file format during the Save As process. Google Chrome now includes printing to a PDF file from the Print menu. The operating system on an Apple computer can Save As a PDF from its standard print menu.
Applications
Applications are a form of software, but not all software is an application. System software controls the operational and processing functions on your computer. Also called a program, application software is designed to perform a specific task. Some applications are pre-installed on computers, but additional software must be installed by the user. Examples include programs like databases, word processing like Microsoft Word and Excel, multimedia editing software like Adobe Photoshop and Premiere Pro, to virus protection software like McAfee.
Driver software empowers your computer to communicate with your operating system (OS), as well as your files. programs, connected components, and external add-ons like your keyboard, mouse, and printer. It is essential you have the proper driver installed on your computer when connecting to additional hardware. It is best practice to consult the technology support at your school if issues arise.
Application software is often designated between desktop and web-based or mobile applications. Desktop and web-based applications generally have broader functionality. Mobile applications are designed to perform on mobile devices.
Pricing!
Software prices range from free to very expensive. Typically the more robust the application, the more it costs. When purchasing software a user must decide how many features they are looking for and how much they want to spend. There are various technologies and applications that exist that are both free and paid.
Installing Applications (Software)
Application software can be purchased from a physical store or online. When bought from the store, you typically receive a box with directions and an installation CD. Installation this way is relatively user-friendly. You insert the CD and follow the installation wizard.
The most common way to get software is to download it from the Internet (purchased). The installation is similar when getting software directly off the Internet, whether it is open source or purchased software. Software is installed on your computer using the installer file, typically a .exe file on a PC or a .dmg file on a Mac. The installer file will be available on the website and must first be downloaded to the computer. Once downloaded, the installer can run and install the application to the hard drive.
Installation on a Mac is a little different than installation on a PC. Further, installation can vary depending on the specific software. However, a basic understanding provides the tools and techniques for installing most products.
The two applications types are:
- Commercial (Paid)
- Open Source (Free)
Version
Software updates frequently update, and updates are typically available for free on the web. This is the advantage of getting software by downloading it from the web; you get the most recent version. Regarding software updates, each software improvement is assigned a number. So when the established software version, say 1.5.3, improves, the next version will be 1.5.4. Generally, the following describes changes:
- Major number, or first number change, indicates changes in overall functionality (1.5 to 2.1)
- Minor number changes or second-level numbers indicate minor changes or fixes (1.5 to 1.6)
- Revision number, or third-level, changes indicate minor bugs or fixes (1.5.3 to 1.5.4)
Browsers
A browser is a computer program with a graphical user interface for displaying and navigating between web pages. This software allows a computer user to find and view information on the Internet. Web browsers interpret the HTML tags in downloaded documents and format the displayed data according to standard style rules (Gregersen, E., 2016).
Video: HTML Explained in 5 Minutes
- Video: What is HTML, CSS, and Javascript?
-
- The next video is longer and provides more detail to HTML, CSS, and Javascript.
-
Each browser may have slightly different options available. Knowing what the browser offers and what capabilities you desire is essential. Browser tools can play a part in your decision. Examples of tools on some of the top browsers include saving passwords and/or syncing passwords, bookmarking, tabs, voice-reading of websites, etc. Chrome offers extensions and tiny programs that add new features to your browser and personalize your browsing experience.
Many different types of browsers exist. As long as the computer meets the browser requirements, a computer can have more than one browser installed. A list of the most common Internet browsers is listed below:
-
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Mozilla Firefox is a free browser for both Mac and PCs, it functions very similar to Microsoft Edge (the replacement for Internet Explorer) which comes pre-installed on Windows machines and Safari which comes pre-installed on Mac devices. Each browser has its advantages and disadvantages, but two are better than one. One of the first steps to try when troubleshooting Internet problems is to try a different browser. Having two browsers installed allows you to do this. Since both Macs and PCs have a pre-installed browser and Firefox works on both, it’s a good solution as a second browser.
- Opera
- Apple Safari
- Microsoft Edge
Additional Internet browsers exist. In the world of Big Tech, one may prefer to search the Internet without personalized browsing, often seen in major search engines (Google, for example). In this case, DuckDuckGo is a good option for an Internet browser. Read this article from CNET on how to use the DuckDuckGo search engine.
-
Assignments
- What file types are you familiar with? What file types are new?
- In your experience, what file types have you used before, and for what purpose(s)?
- Browser Wars! Make a chart comparing the three best Internet Browsers (in your opinion). Do your research for this assignment! A few things you can start with include: What are the similarities between browsers? What makes one stand out over the other? Which OS is the browser compatible with? How fast is the browser? Which one would you choose for your students?
References
Ibm. (2025, January 7). What is computer networking? IBM. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/networking
Media Attributions
- Windows and Mac OS Table
- file types