9.1 What Is a Group?
[Author removed at request of original publisher]
As humans, we are social beings. We naturally form relationships with others. In fact, relationships are often noted as one of the most important aspects of a person’s life, and they exist in many forms. Interpersonal communication occurs between two people, but group communication may involve two or more individuals. Groups are a primary context for interaction within the business community. Groups may have heroes, enemies, and sages alongside new members. Groups overlap and may share common goals, but they may also engage in conflict. Groups can be supportive or coercive and can exert powerful influences over individuals.
Within a group, individuals may behave in distinct ways, use unique or specialized terms, or display symbols that have meaning to that group. Those same terms or symbols may be confusing, meaningless, or even unacceptable to another group. An individual may belong to both groups, adapting his or her communication patterns to meet group normative expectations. Groups are increasingly important across social media venues, and there are many examples of successful business ventures on the Web that value and promote group interaction.
Groups use words to exchange meaning, establish territory, and identify who is a stranger versus who is a trusted member. Are you familiar with the term “troll”? It is often used to identify someone who is not a member of an online group or community; does not share the values and beliefs of the group; and posts a message in an online discussion board to initiate flame wars, cause disruption, or otherwise challenge the group members. Members often use words to respond to the challenge that are not otherwise common in the discussions, and the less than flattering descriptions of the troll are a rallying point.
Groups have existed throughout human history and continue to follow familiar patterns across emerging venues as we adapt to technology, computer-mediated interaction, suburban sprawl, and modern life. We need groups, and groups need us. Our relationship with groups warrants attention on this interdependence as we come to know our communities, our world, and ourselves.
We form self-identities through our communication with others, and much of that interaction occurs in a group context. A group may be defined as three or more individuals who affiliate, interact, or cooperate in a familial, social, or work context. Group communication may be defined as the exchange of information with those who are alike culturally, linguistically, and/or geographically. Group members may be known by their symbols, such as patches and insignia on a military uniform. They may be known by their use of specialized language or jargon; for example, someone in information technology may use the term “server” in reference to the Internet, whereas someone in the food service industry may use “server” to refer to the worker who takes customer orders in a restaurant. Group members may also be known by their proximity, as in gated communities. Regardless of how the group defines itself, and regardless of the extent to which its borders are porous or permeable, a group recognizes itself as a group. Humans naturally make groups a part of their context or environment.
Types of Groups in the Workplace
As a skilled business communicator, learning more about groups, group dynamics, management, and leadership will serve you well. Mergers, forced sales, downsizing, and entering new markets all call upon individuals within a business or organization to become members of groups. Think of some of the professional (i.e., work-related) groups you interact with in order of frequency. What does your list include? Perhaps you noted your immediate coworkers, your supervisor and other leaders in your work situation, members of other departments with whom you communicate, and the colleagues who are also your personal friends during off-work times. Groups may be defined by function. They can also be defined, from a developmental viewpoint, by the relationships within them. Groups can also be discussed in terms of their relationship to the individual and the degree to which they meet interpersonal needs.
Some groups may be assembled at work to solve problems, and once the challenge has been resolved, they dissolve into previous or yet-to-be-determined groups. Functional groups like this may be immediately familiar to you. You take a class in business communication from a professor of business communication, who is a member of the discipline of business communication. To be a member of a discipline is to be a disciple, and adhere to a common framework for viewing the world. Disciplines involve a common set of theories that explain the world around us, terms to explain those theories, and have grown to reflect the advance of human knowledge. Compared to your BCOM210 business communication instructor, your health and physical performance instructor may see the world from a completely different perspective. Still, both may be members of divisions or schools, dedicated to teaching or research, and come together under the large group heading we know as the university.
In business, we may have marketing experts who are members of the marketing department, who perceive their tasks differently from a member of the sales staff or someone in accounting. You may work in the mailroom, and the mailroom staff is a group in itself, both distinct from and interconnected with the larger organization.
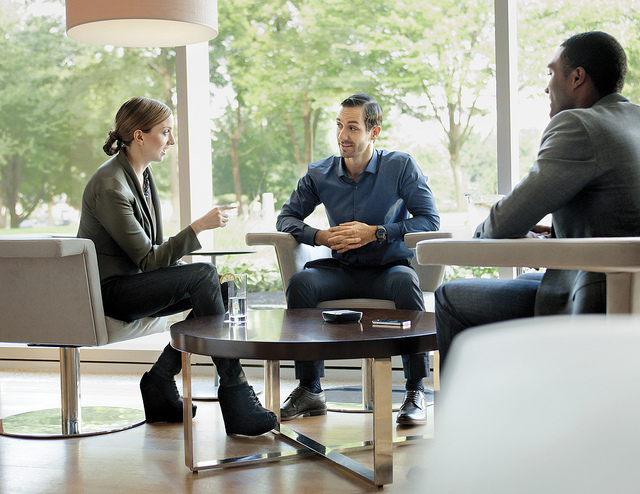
Figure 9.1
Groups and teams are an important part of business communication.
plantronicsgermany – calisto_620_group_conference_crop – CC BY-ND 2.0.
Relationships are part of any group and can be described in terms of status, power, control, as well as role, function, or viewpoint. Within a family, for example, the ties that bind you together may be common experiences, collaborative efforts, and even pain and suffering. The birth process may forge a relationship between mother and daughter, but it also may not. An adoption may transform a family. Relationships are formed through communication interaction across time and often share a common history, values, and beliefs about the world around us.
In business, an idea may bring professionals together and they may even refer to the new product or service as their “baby,” speaking in reverent tones about a project they have taken from the drawing board and “birthed” into the real world. As in family communication, work groups or teams may have challenges, rivalries, and even “birthing pains” as a product is developed, adjusted, adapted, and transformed. Struggles are a part of relationships, both in families and business, and form a common history of shared challenges overcome through effort and hard work.
Through conversations and a shared sense that you and your coworkers belong together, you meet many of your basic human needs, such as the need to feel included, the need for affection, and the need for control (Schutz, 1966). In a work context, “affection” may sound odd, but we all experience affection at work in the form of friendly comments like “good morning,” “have a nice weekend,” and “good job!” Our professional lives also fulfill more than just our basic needs (i.e., air, food, and water, as well as safety). While your workgroup may be gathered together with common goals, such as delivering the mail in a timely fashion to the corresponding departments and individuals, your daily interactions may well go beyond this functional perspective.
In the same way, your family may provide a place for you at the table and meet your basic needs, but they also may not meet other needs. If you grow to understand yourself and your place in a way that challenges group norms, you will be able to choose which parts of your life to share and to withhold in different groups, and to choose where to seek acceptance, affection, and control.
Workgroups typically have the goal to complete a task or solve a problem. If you are a member of the sales department, your purpose is to sell. In terms of problem-solving, work groups can accomplish more than individuals can. People, each of whom has specialized skills, talents, experience, or education, come together in new combinations with new challenges to find new perspectives to create unique approaches that they themselves would not have formulated alone.
Group norms are customs, standards, and behavioral expectations that emerge as a group forms. If you post an update every day on your Instagram and your followers stop by to like and comment, not posting for a week will violate a group norm. They will wonder if you are sick or somewhere you have no access to your phone to keep them updated. If, however, you only post once a week, the group will come to naturally expect your customary post. Norms involve expectations that are self and group imposed and that often arise as groups form and develop.
If there are more than eight members in a group, it becomes a challenge to have equal participation, where everyone has a chance to speak, listen, and respond. Some will dominate, others will recede, and smaller groups will form. Finding a natural balance within a group can also be a challenge. Small groups (3 to 8 people) need to have enough members to generate a rich and stimulating exchange of ideas, information, and interaction, but not so many people that what each brings cannot be shared (Galanes, Adams & Brilhart, 2000).